1. 简介
策略模式用于避免编写开发者在方法里使用大量的 If-Else 语句,将使用算法的责任和算法本身分割开来,委派给不同的对象管理,提升代码可读性以及可维护性。
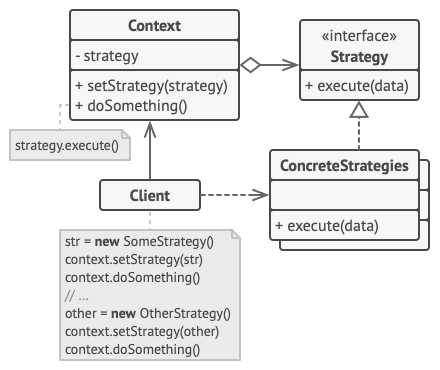
- 上下文 (Context) 维护指向具体策略的引用, 且仅通过策略接口与该对象进行交流。
- 策略 (Strategy) 接口是所有具体策略的通用接口, 它声明了一个上下文用于执行策略的方法。
- 客户端 (Client) 会创建一个特定策略对象并将其传递给上下文。 上下文则会提供一个设置器以便客户端在运行时替换相关联的策略。
- 当上下文需要运行算法时, 它会在其已连接的策略对象上调用执行方法。 上下文不清楚其所涉及的策略类型与算法的执行方式。
Spring 框架中使用策略模式
spring 中对于策略模式模式的实现,可以利用 spring 框架关于 Map 类型的自动装配特性。
以 refactoringguru 网站上的 Navigator 为实例,进行思路分析。
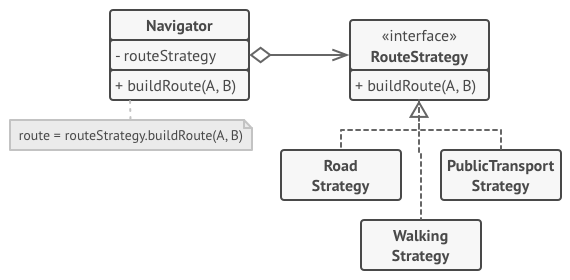
定义接口
1 | public interface RoutingStrategy { |
RoadStrategy 实现类
1 | ("RoadStrategy") |
PublicTransportStrategy 实现类
1 | ("PublicTransportStrategy") |
WalkingStrategy 实现类
1 | ("WalkingStrategy") |
每个实现类分别实现 RoutingStrategy 接口,并使用 @Component 注解将实现类注入到 spring 容器中。
RoutingController 使用 Map<String, RoutingStrategy> 获得 spring 容器中全部实现 RoutingStrategy 接口的实例。
此外,Map 中 key 的值对应上文使用 @Component 注入是为实现类设置的名称。
1 |
|
依据 Web API 传入的 type,在 routingStrategies 字典找到对应的策略实现类,并通过实现类中独立封装的算法逻辑,返回需要的 Route 对象。
spring 集合类型注入知识补充
spring 框架处理集合类型自动装配的源码位于 DefaultListableBeanFactory 类的 resolveMultipleBeans 方法。
1 |
|
1. if (type.isArray()) 分支
如果需要装配的对象类型为数组,通过 findAutowireCandidates 方法在 Spring IOC 容器中找到与数组成员类型匹配的 bean。
并将找到的 bean 放置在数组中,返回给装配对象。
1 | RoutingStrategy[] routingStrategies; |
routingStrategies 的成员为 RoadStrategy, PublicTransportStrategy, WalkingStrategy。
2. Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(type) && type.isInterface() 分支
1 | List<RoutingStrategy> routingStrategies; |
与数组处理逻辑类似,处理 Java 集合的装配对象,但是要求集合中成员的类型为接口。
3. Map.class == type 分支
对应上文 Map<String, RoutingStrategy> routingStrategies 自动装载。Spring 会将 bean 名称设置为 key,并将 bean 的引用设置为对应的 value。